To learn more about our Diabetes Self-Management Education program:

After a person eats, the food becomes glucose (blood sugar). That glucose needs to get into the cells and the muscles to provide energy for the body.

The cells act like a lock and the pancreas makes a hormone, called insulin, which is the key that can unlock those cells.
The challenge for those with diabetes is that the pancreas doesn’t make enough insulin or doesn’t use it as well as it should. The result is too much glucose that stays in the blood.
High amounts of glucose in the blood can cause serious health problems such as vision loss, kidney disease, numbness in the fingers and toes, heart disease, and many other challenges.



Type 1 diabetes- For individuals with type 1 diabetes, the body makes little to no insulin. This used to be known as Juvenile Diabetes because most people are diagnosed as children or young adults. Individuals with type 1 will need to take insulin every day.

For individuals with type 2 diabetes, the body doesn’t use insulin well and can’t keep glucose (blood sugar) at normal levels. Type 2 diabetes develops over the course of many years and is generally diagnosed in adults.
This affects pregnant women who cannot produce enough insulin or the body doesn’t use insulin properly. Resulting in too much glucose (blood sugar) remaining in the blood that could create pregnancy complications. Most of the time, blood sugars return to normal after childbirth.
Type 2 diabetes can be prevented or delayed with healthy lifestyle changes such
as the Diabetes Prevention Program.
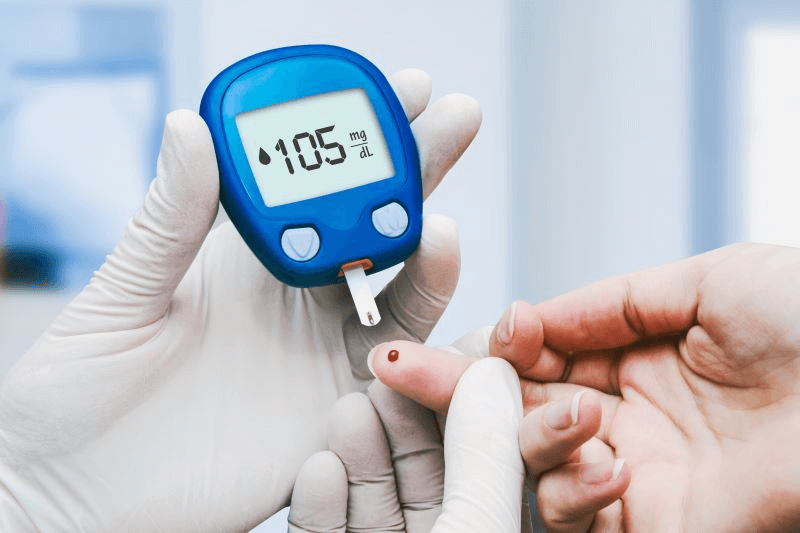
The Diabetes Self-Management Education (DSME) program is a 6 week program that gives participants the tools to monitor glucose at home, make lifestyle changes, learn valuable information on medications and insulin, and make informed choices about foods and carbohydrates to manage diabetes. The program is accredited by the Association of Diabetes Care and Education Specialists (ADCES) and participants in the program have an average reduction in A1c of 1.15!
Registration is required and
This Number is Toll Free
Copyright 2022 GIFT Get Into Health Today! / All Right Reserved - Powered By Wethink Marketing